Mastering Leukocyte Identification: Identify the Leukocytes in the Figure in Order to
Understanding Leukocytes
Leukocytes have a crucial purpose in the human body, acting as the body’s primary line of defense against infections and diseases. Their presence and activities are a reliable indicator of health. It’s because of this that identifying and understanding the various types of leukocytes becomes paramount.
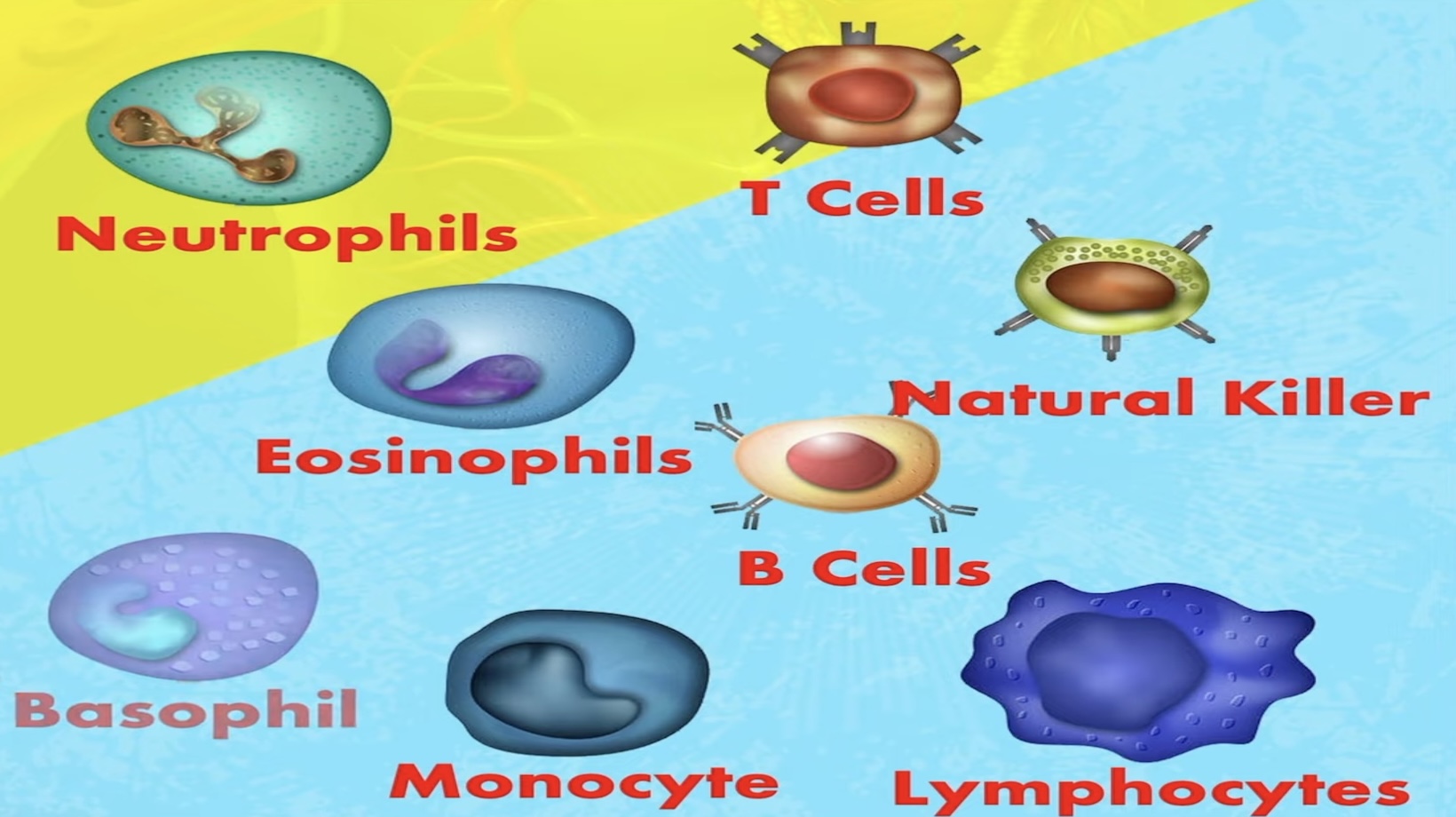
There are five main types of leukocytes each with their unique functions. These include neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. When doctors refer to white blood cell count, they’re usually referring to these five types.
Knowing and identifying each type of leukocyte provides a clear picture of what is happening in your body. For example, a rise in the level of certain leukocytes could indicate an infection or an immune response to a specific condition. It’s like having a finger on the pulse of your immune system!
Role of Leukocytes in the Body
The primary function of leukocytes is to fight infections and diseases in the body. This makes them central to our immune system. They’re like the body’s little soldiers on the frontline.
Leukocytes are responsible for identifying and eliminating pathogens. In the event of an infection, the number of leukocytes in your body tends to increase, making it easy to detect an ongoing battle against an infection.
Neutrophils, a type of leukocyte, are usually the first to arrive at the site of an infection. They’re quick responders, racing to engulf and destroy the invading pathogens. On the other hand, lymphocytes help in producing antibodies, which are proteins specifically designed to neutralize particular pathogens.
Maintaining a healthy leukocyte count is also essential for overall health. If your body has too few leukocytes, you’ll be more prone to infections. On the flip side, an unusually high number could indicate an underlying health issue that’s causing your immune system to overreact.
It’s clear that leukocytes are not just mere cells floating in your bloodstream. They’re complex fighting machines that benefit us in more ways than one. It’s what makes understanding these cells and their roles in your health, so important and fascinating.
Identify the Leukocytes in the Figure in Order to
As highlighted earlier, the human body has five main types of leukocytes. Each plays a significant role in fending off infections and maintaining overall health. Recognizing these different leukocyte types equips us with a better understanding of our immune system and overall health.
Neutrophils
Neutrophils spearhead the body’s immune defense. They’re the most abundant type of leukocytes and are the body’s first line of defense when an infection strikes. Neutrophils respond rapidly to invaders by engulfing and neutralizing them. They’re highly equipped to tackle bacteria and fungi, making them a crucial asset in white blood cell categorization.
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes add a sophisticated layer to the body’s immune capabilities. They come in two main types: B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes. B-lymphocytes produce antibodies, proteins specifically crafted to neutralize certain pathogens. On the other hand, T-lymphocytes of the self of non-self cells and attack foreign and cancer cells.
Monocytes
Another significant leukocyte type is Monocytes. They make up a smaller percentage of the white blood cell count, but their role is just as vital. These cells transform into macrophages and dendritic cells which play a key role in consuming bacteria, dead cells, and other debris in our body.
Eosinophils
Eosinophils are a special type of leukocytes that primarily deal with allergy responses and parasitic infections. They’re a formidable force, particularly during inflammatory responses and in the fight against larger parasite invasions. While these constituents are less abundant, they can significantly increase during an allergic reaction or a parasitic infection.
Basophils
Finally, Basophils stand as the rarest among leukocytes—comprising less than 1% of the white blood cell count. Despite their small number, their influence is far-reaching. They’re especially active during allergic reactions, where they secrete substances like histamine and heparin. These substances intensify the inflammatory response and prevent blood clotting, respectively, contributing significantly to the body’s immune reaction.
We will proceed by delving into how exactly these leukocytes identify and respond to diverse threats in the next section.
Note that identifying these cells in a numerical order can be challenging without proper medical knowledge and microscopic studies. Hence, seeking professional medical advice is always suggested.



















































































